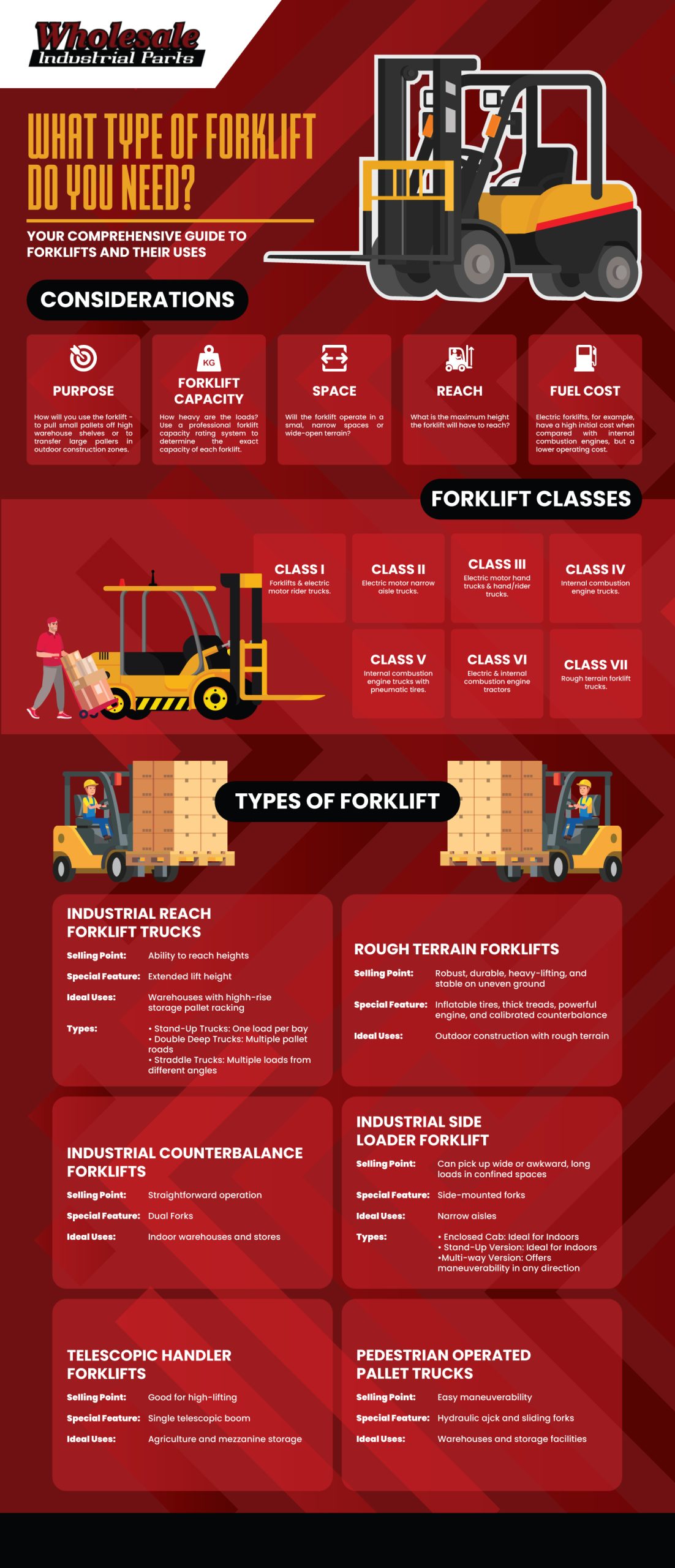
Most people assume that there are only two forklift classifications: side-loaders and lift trucks. However, there are different types of forklifts. It can be broken down into seven other forklift classes, confusing even an inexperienced individual.
Knowing how many classes of forklifts are there and understanding the differences between each forklift class is crucial to choosing the right equipment for your operation. This guide will help you understand the different classes of forklifts and how to choose the best fit for your next project.
Class I. Electric Motor Rider Trucks
As the name suggests, Class I forklift trucks use electric motors. The operator can stand up if it is a counterbalanced type wherein the heaviest section is found in its rear part housing its heavy battery.
If it is a three-wheel type, then operators will have the opportunity to sit down while operating the machine. Another variant is a counterbalanced rider with a sit-down feature with a cushion tire, pneumatic, or a combination of both types.
Cushion tires are perfect for smooth surfaces like asphalt and concrete. They have a much softer surface and provide gentle rolling, which makes them less likely to cause surface damage.
The advantage of this type of forklift is that it does not require a large footprint. Thus, one can squeeze into smaller spaces more quickly than other types of forklifts.
Pneumatic tires, on the other hand, are designed for outdoor applications and heavier product loads. So instead of solid rubber, the wheel tubes have air in them. It allows them to be lighter, run cooler and make it easier for drivers to avoid bumpy surfaces.
The last type of forklift for this Class is the combination of these two kinds of tires. The cushion reduces the impact on the load it lifts, while the pneumatic tire allows for excellent traction and control when moving around with heavy loads.
Class II. Electric Motor Narrow Aisle Trucks
They are powered by an electric motor, meaning they do not need to be connected to a power source and can still operate in an enclosed space. As a result, warehouses, distribution centers, manufacturing plants, and indoor environments with little or no room for the truck to turn around use this Class of forklift.
High Lift Straddle
It can lift loads too tall or large for the forklift to reach with its forks.
Order Pickers
These are ideal for retrieving items, such as pallets or individual orders, from the warehouse and delivering them to the shipping area.
Reach Type Outrigger
This type of forklift allows operators to change the reach of trucks by adjusting the length of the forks to lift loads farther away or lower them closer to the ground.
Side Loader Forklifts
The loading container is attached to its side, as opposed to being at the front or rear of the vehicle, like most other forklifts. In addition, they come in two features: solid base platforms and high-lift pallets.
Turret Tracks
They feature a rotating mast that allows the forklift to turn left or right. The operator controls the mast using a joystick, and it can be raised or lowered by pressing buttons on the joystick.
Low Lift
The low profile is ideal for tight spaces other forklift types cannot reach, such as in small warehouses or unloading docks.
Class III. Electric Motor Hand or Hand/Rider Trucks
The low-lift forklift types can load or unload the pallet as little as possible. It allows for a safe, controlled motion that reduces stress on the machine while keeping a good view of what is happening around it.
They can be driven or operated by hand. It may feature a platform as a solid base and a walkie pallet with a pair of forks. The control mechanism can be center– or end-controlled depending on the location of the steering wheel.
When other forklift types‘ standard reach is insufficient to reach the desired load, operators should use hand-operated high-lift forklifts.
Reach-type outriggers can provide maximum reach while still being able to lift heavy loads. The outriggers on this type of forklift allow the operator to access areas that are typically out of reach.
For shipping containers and other oversized loads that need to move around frequently, single-face pallets can lift them out of the container in storage.
Class IV. Internal Combustion Engine Trucks. Cushion Tires
These trucks use a combustion engine to power the machine. The typical fuels used are diesel, gasoline, propane, and other types of natural gases.
It has a counterbalanced feature wherein the weight is at the rear of a forklift. As a result, it allows for more excellent stability when lifting and lowering loads and effortless handling of pallets or other large objects.
Under this Class, the trucks will have cushion tires. These tires absorb shock and damping vibrations, making them effective in high-traffic areas or around sensitive equipment.
Class V. Internal Combustion Engine Trucks. Pneumatic Tires
The only difference between this forklift class and Class IV is that these trucks have pneumatic tires. Pneumatics cannot be punctured, making them great for use on rough terrains like gravel or dirt.
The initial purchase may be expensive, but they do not require frequent replacement. It also requires less maintenance than cushion tires, saving owners money in the long run.
Class VI. Electric and Internal Combustion Engine Tractors
This forklift can lift over 999 pounds or 453 kilograms. A weight test determines this number, which measures the maximum amount of allowed weight without causing damage to the equipment.
Electric tractors will have electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. As for the internal combustion engine tractors variant, they run on gasoline or diesel fuel.
Class VII. Rough Terrain Forklift Trucks
Special tires and suspension systems make them capable of operating in areas with high ground clearance, limited traction, and other conditions that otherwise make using any different regular forklift classifications impossible.
Get Best Value For Foklift’s Parts, Services, and Solutions
Forklifts are one of the most common pieces of equipment used in warehouses and distribution centers worldwide. Therefore, knowing how many classes of forklifts are there and which one you need is vital to operate safely.
At Wholesale Industrial Parts, we are committed to providing high-quality forklift parts and services to our clients in different classes of forklifts. In addition, our experienced technicians can help you diagnose problems with your forklift and recommend the right solution. For any concerns or questions, feel free to email us at info@wiparts.net or call us at (844) 588-8455.
